Schools Interoperability Framework™
SIF Infrastructure Implementation Specification 2.5
February 2, 2011
- This version:
-
http://specification.sifassociation.org/Implementation/2.5/infrastructure/2/
- Previous version:
-
http://specification.sifassociation.org/Implementation/2.4/
- Latest version:
-
http://specification.sifassociation.org/Implementation/
- Schemas
-
SIF_Message (single file, non-annotated)
(ZIP archive)
-
Note:
SIF_Message schemas define every data object element as optional per SIF's Publish/Subscribe and SIF Request/Response Models;
DataModel schemas maintain the cardinality of all data object elements.
Please refer to the errata for this document, which may include some normative corrections.
This document is also available in these non-normative formats: ZIP archive, PDF (for printing as a single file),
Excel spreadsheet.
Copyright ©2011
Schools Interoperability Framework (SIF™) Association. All Rights Reserved.
1 Preamble
1.1 Abstract
1.1.1 What is SIF?
The Schools Interoperability Framework (SIF) is not a product, but a technical blueprint for enabling diverse
applications to interact and share data related to entities in the pK-12 instructional and administrative environment. SIF is designed to:
- Facilitate data sharing and reporting between applications without incurring expensive customer development costs;
- Enhance product functionality efficiently; and
- Provide best-of-breed solutions to customers easily and seamlessly.
The SIF Implementation Specification defines:
- an XML-based messaging framework that allows diverse software applications to interoperate and share and report data related to entities
in the pK-12 instructional and administrative environment;
- an HTTP(S)-based transport for conveying these SIF messages;
- an abstract, platform-independent definition of a message queue for reliable delivery of asynchronous SIF messages and related synchronous
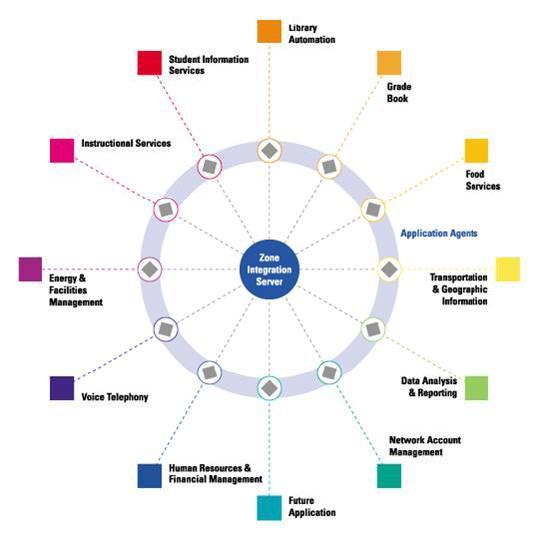
administrative functions—the Zone Integration Server (ZIS); and
- an abstract, platform-independent definition of the interface between a software application and the ZIS—the SIF Agent.
These are known collectively as the SIF Infrastructure. The SIF Implementation Specification also defines the SIF Data Model:
- an XML-based data model that models entities in the pK-12 environment as SIF Data Objects to be shared between applications.
A SIF Zone is a distributed system that consists of a ZIS and one or more software applications
with a SIF Agent (a SIF-enabled application) sharing/reporting one or more SIF data objects over a network.
A SIF Implementation consists of one or more SIF Zones deployed and configured to meet customer data sharing and reporting needs.
The SIF Implementation Specification defines architecture requirements and communication protocols for software components and the interfaces
between them; it makes no assumption of specific hardware or software products needed to develop SIF-enabled applications and Zone Integration Server implementations,
other than their ability to support technologies leveraged as the foundation for SIF, most prominently XML and HTTP(S).
1.1.2 Schools Interoperability Framework Association
The Schools Interoperability Framework Association (SIF Association) is an industry initiative to enable interoperability and data sharing between
software applications in the pK-12 instructional and administrative environment, and the forum for companies and educators to participate
in the development of SIF specifications in the SIF Association's working groups and task forces. The SIF Association is designed to:
- Join industry leaders in creating the next-generation framework for education technology; and
- Leverage co-marketing opportunities with partners and distributors.
1.2 Disclaimer
The information, software, products, and services included
in the SIF Implementation Specification may include inaccuracies or typographical errors. Changes are periodically added to the information herein. The SIF Association may make improvements and/or changes in this document at any time without notification. Information contained in this document should not be relied upon for personal, medical, legal, or financial decisions. Appropriate professionals should be consulted for advice tailored to specific situations.
THE SIF ASSOCIATION, ITS PARTICIPANT(S), AND THIRD PARTY CONTENT PROVIDERS MAKE NO REPRESENTATIONS ABOUT THE SUITABILITY, RELIABILITY, TIMELINESS, AND ACCURACY OF THE INFORMATION, SOFTWARE, PRODUCTS, SERVICES, AND RELATED GRAPHICS CONTAINED IN THIS DOCUMENT FOR ANY PURPOSE. ALL SUCH INFORMATION, SOFTWARE, PRODUCTS, SERVICES, AND RELATED GRAPHICS ARE PROVIDED "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND. THE SIF ASSOCIATION AND/OR ITS PARTICIPANT(S) HEREBY DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES AND CONDITIONS WITH REGARD TO THIS INFORMATION, SOFTWARE, PRODUCTS, SERVICES, AND RELATED GRAPHICS, INCLUDING ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES AND CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, TITLE, AND NON-INFRINGEMENT.
IN NO EVENT SHALL THE SIF ASSOCIATION, ITS PARTICIPANT(S), OR THIRD PARTY CONTENT PROVIDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, PUNITIVE, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, OR ANY DAMAGES WHATSOEVER INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS, ARISING OUT OF OR IN ANY WAY CONNECTED WITH THE USE OR PERFORMANCE OF THIS DOCUMENT, WITH THE DELAY OR INABILITY TO USE THE DOCUMENT, THE PROVISION OF OR FAILURE TO PROVIDE SERVICES, OR FOR ANY INFORMATION, SOFTWARE, PRODUCTS, SERVICES AND RELATED GRAPHICS OBTAINED THROUGH THIS DOCUMENT OR OTHERWISE ARISING OUT OF THE USE OF THIS DOCUMENT, WHETHER BASED ON CONTRACT, TORT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR OTHERWISE, EVEN IF THE SIF ASSOCIATION, ITS PARTICIPANT(S), OR THIRD PARTY CONTENT PROVIDERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF DAMAGES. BECAUSE SOME STATES/JURISDICTIONS DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, THE ABOVE LIMITATION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU. IF YOU ARE DISSATISFIED WITH ANY PORTION OF THIS DOCUMENT OR WITH ANY OF THESE TERMS OF USE, YOUR SOLE AND EXCLUSIVE REMEDY IS TO DISCONTINUE USING THIS DOCUMENT.
This specification is released with the following provisos to developers and educators.
1.3 Certification and Compliance Claims
Though a product may be demonstrated to comply with this specification, no product may be designated as
SIF Certified™ by an organization
or individual until the product has been tested against and
passed established compliance criteria, published separately [SIFCertification].
Organizations and individuals that are currently paying annual membership dues to the SIF Association
and dedicating resources to the initiative may also use the designation
SIF Participant to describe their involvement with the SIF Association and SIF in marketing, public relations and other materials.
Full Table of Contents
2.4.2
2.4.3
2.4.4

